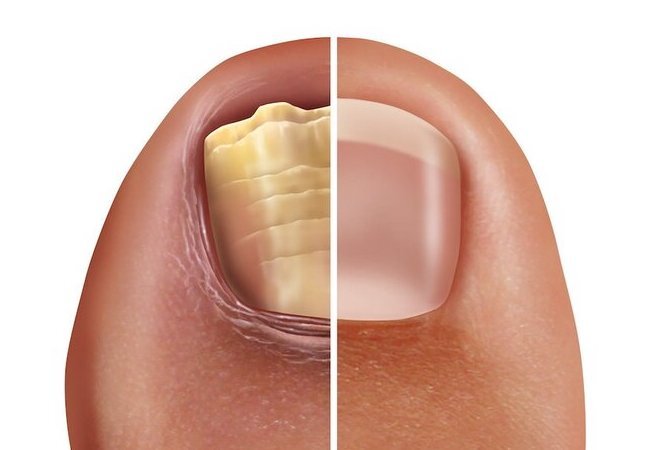
Fungal nail infection, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The infection is caused by various types of fungi that grow on the nail plate, causing the nail to become thick, discolored, and brittle. Fungal nail infections can be challenging to treat, and often require a combination of therapies for effective management. In this article, we will discuss the effectiveness of combination therapies for fungal nail infection.
Combination therapies involve the use of two or more treatments to improve the outcome of the therapy. The combination therapies can be topical, oral, or a combination of both. The goal of combination therapy is to increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the risk of relapse. Studies have shown that combination therapies are more effective than single therapies in the treatment of fungal nail infection.
Topical and oral antifungal medications are commonly used to treat fungal nail infections. Topical antifungal agents are applied directly to the infected nail, while oral antifungal medications are taken orally. Topical antifungal agents include ciclopirox, efinaconazole, tavaborole, and amorolfine. Oral antifungal agents include terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole.
Studies have shown that the combination of topical and oral antifungal medications is more effective than either treatment alone. The combination of terbinafine and amorolfine has been shown to be particularly effective in the treatment of fungal nail infection. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that the combination of oral terbinafine and topical amorolfine resulted in a mycological cure rate of 93.3% and a clinical cure rate of 86.7%.
Another study published in the British Journal of Dermatology found that the combination of oral itraconazole and topical ciclopirox was more effective than either treatment alone. The study found that the combination therapy resulted in a mycological cure rate of 81.3% compared to 52.8% for oral itraconazole alone and 43.2% for topical ciclopirox alone.
In addition to antifungal medications, other treatments can be used in combination therapy for fungal nail infection. Laser therapy, which uses a focused beam of light to penetrate the nail plate and kill the fungi, has been shown to be effective in the treatment of fungal nail infection. The combination of laser therapy and antifungal medications has been shown to be more effective than either treatment alone.
Another treatment that can be used in combination therapy for fungal nail infection is debridement. Debridement involves the removal of the infected nail, allowing for better penetration of antifungal medications. The combination of debridement and antifungal medications has been shown to be more effective than either treatment alone.
In conclusion, fungal nail infection can be challenging to treat, and often requires a combination of therapies for effective management. Combination therapies involving topical and oral antifungal medications, laser therapy, and debridement have been shown to be more effective than either treatment alone. If you have a fungal nail infection, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Source: Fungal nail treatment